The process of forming an LLC is rather straightforward, however, having the advantages and disadvantages organised gives one a better understanding and helps to make an informed decision so much easier. It also prevents information overload by stating the bare facts.
What are the advantages?
- Personal Asset Protection
In the event of there not being any fraud or criminal behaviour, then the owners of an LLC will not be held personally responsible for any of the debts or lawsuits incurred by the LLC. One needs to realize that the LLC protects only the assets, therefore having general liability insurance will protect the assets of a business in the event of the business being involved in a lawsuit.
- Saving on double tax
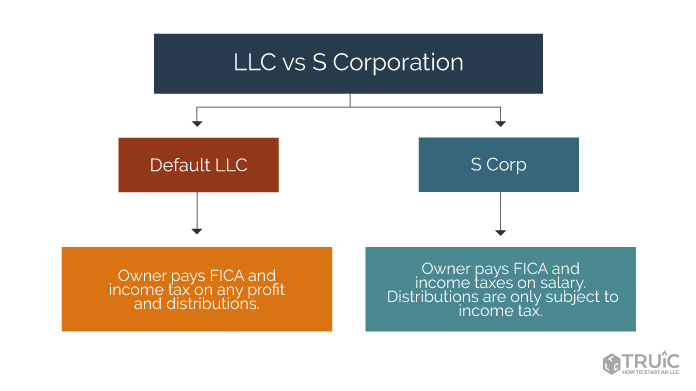
The profits of an LLC go directly to its owners, and the owners are responsible for reporting their share of the profits on their tax returns. Therefore, LLC’s are only taxed once, a term referred to as pass-through taxation. This is compared to the tax method used in C corporation, where profits are subject to being doubled-taxed. In this method, profits are taxed before being distributed to its owners and will be subjected to tax once again when the owners are expected to report their share of profits when submitting their tax returns. It is recommended to carry out further research into c corp vs llc to ensure you get a good understanding of the difference.
- Simplicity
LLCs are relatively easy to form and maintain as it requires little paperwork. When comparing it to C-Corporations, LLC does not need to be assigned formal officer roles, they are not expected to hold annual meetings, or even record company minutes and resolutions.
- Flexibility
There are few restrictions on how to structure the ownership and management of the LLC. An LLC can consist of a single-member or multi-member. When utilizing a multi-member LLC, it means that the LLC will be managed by the members, also known as member-managed. The other option is that multi-member LLC can be managed by the appointed manager as set out by the members, this is referred to as manager-managed. The other addition is that LLC has the option of electing to be taxed as either a C-Corporation or an S-Corporation, whichever is more beneficial.
- Increased Credibility
Choosing to form an LLC brings added credibility. LLC is recognized as a more formal business structure than a sole proprietorship or partnership. Incorporating LLC in the business name lets customers and partners know that it is a credible business.
- Access Business Loans
Forming an LLC allows for the business to start building a credit history.
What are the disadvantages?
- Lack of strict requirements gives the impression that LLC’s have less structure. Also, not having a detailed operating agreement in place has the potential to cause issues down the line, which could incur additional upfront costs such as attorney fees.
- The owners of the LLC need to pay their taxes on their share of the LLC income. Often investors will not fund LLC’s, as a result of the fact that members of the LLC need to wait until the LLC provides them with the K-1 form, to complete their taxes.
- Considering that LLC’s are controlled by state law, should there be a dispute crossing state boundaries, LLC’s are regarded as partnerships and not corporations. This could then affect how the state court will hear the dispute.
- Transferring ownership of an LLC is often harder to do compared to that of a corporation. Within corporations, there is the option of selling stock. Usually, with LLC’s, all members need to approve the adding of new members.
- LLC’s give investors the luxury of limited liability, but often investors still feel more comfortable investing in more established governance and structure of a corporation.
- Forming and maintaining an LLC can cost more than the sole proprietorship or general partnership. Charges include: initial fee formation, some states also impose ongoing fees; annual report and franchise tax fees. Therefore, it is wise to check this upfront with the Secretary of State’s office
Still contemplating and wanting to learn more? Click here for the latest guide from TRUiC.